Lower Your Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Hypertension Medications
More than 100 million American adults live with high blood pressure, and many don’t even know it. This silent killer often shows no symptoms. It quietly damages your blood vessels and vital organs. Untreated, high blood pressure (hypertension) severely raises your risk for heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, and even vision loss.
Managing high blood pressure is critical for a longer, healthier life. Medication often plays a key role. This guide will help you understand hypertension medications. We’ll cover different types of blood pressure drugs, their common side effects, and how specific classes work. Get ready to take control of your health with clear, easy-to-understand information.
Understanding Your Blood Pressure Numbers and Why They Matter
Knowing your blood pressure numbers is the first step. These numbers show the force of blood against your artery walls.
What is High Blood Pressure?
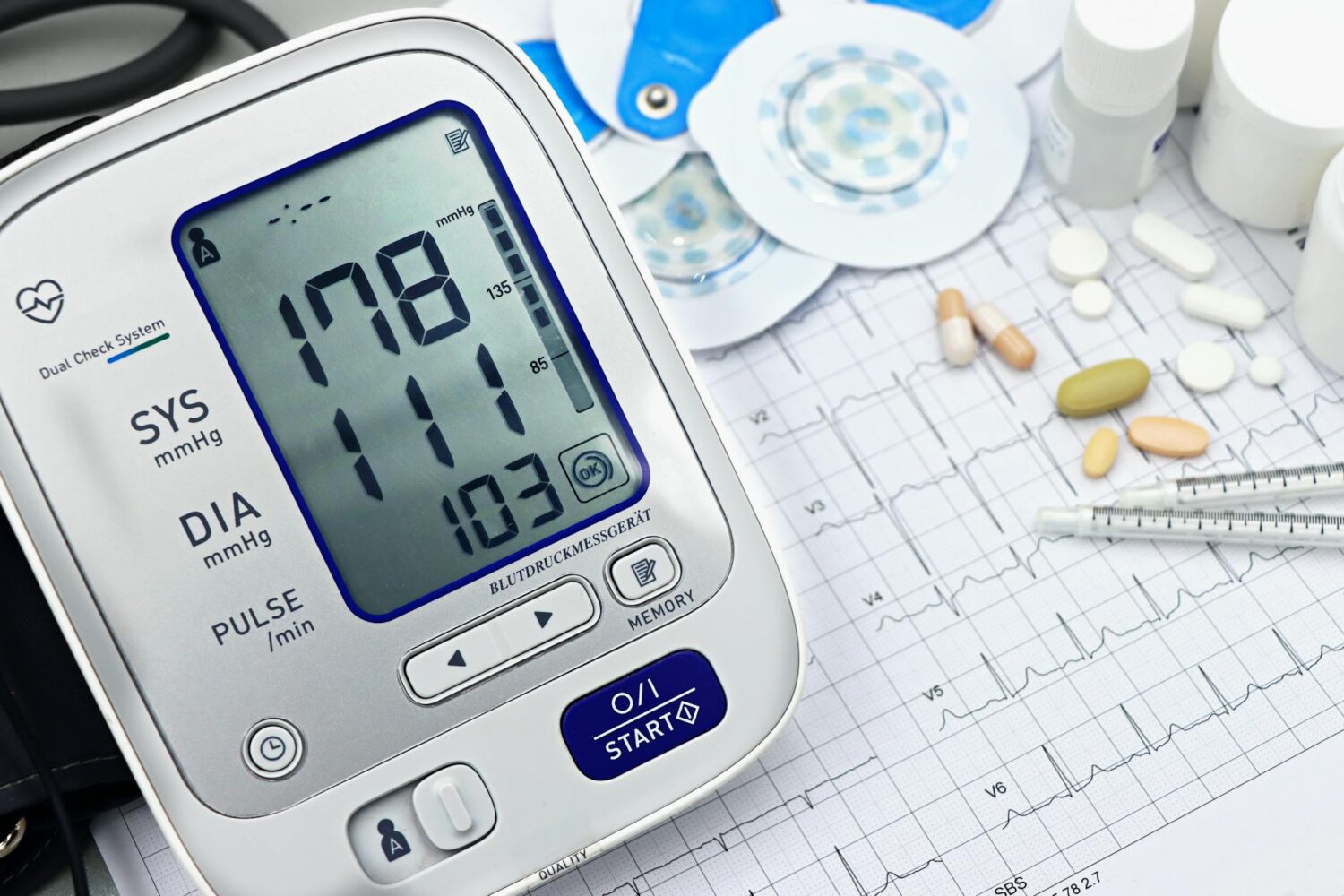
Blood pressure has two numbers. The top number is systolic pressure. It shows the pressure when your heart beats. The bottom number is diastolic pressure. This is the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Normal blood pressure is generally below 120/80 mmHg. “Elevated” falls between 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic. High blood pressure begins at 130/80 mmHg or higher. Regularly checking these numbers helps you and your doctor keep tabs on your health.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure causes major damage. It strains your heart, making it work harder. Your blood vessels become stiff and narrow. This can lead to heart failure, weakened arteries, and even an aneurysm. Kidneys, which filter waste from your blood, can also get damaged. Your eyes might suffer too, leading to vision problems.
Why Medication is Often Necessary
Lifestyle changes are always important for blood pressure control. Eating well, exercising, and reducing stress can make a big difference. But for many, these changes alone are not enough. Your doctor might recommend medication if your blood pressure stays high. This is especially true if you have other health issues or a family history of heart disease.
Treatment for high blood pressure is very personal. What works for one person might not work for another. Your doctor looks at your age, overall health, and other medical conditions. They choose the best medication plan for you. Never self-medicate or stop taking your pills without talking to your healthcare provider.
The Arsenal of Blood Pressure Drugs: A Detailed Look
Doctors have many effective medications to lower blood pressure. Each type works in a different way. Learning about these options can help you understand your treatment better.
Diuretics: Flushing Out Excess Fluid
Often called “water pills,” diuretics are a common first choice. They help your kidneys remove extra sodium and water from your body. This lowers the total amount of fluid in your blood vessels. Less fluid means less pressure, which brings down your blood pressure.
Several kinds of diuretics exist. Thiazide diuretics are widely used. Loop diuretics are stronger and used for more severe fluid buildup. Potassium-sparing diuretics remove fluid but keep potassium in your body. Each type targets different parts of the kidney.
Taking diuretics may lead to more trips to the bathroom. You might also feel dizzy, especially when standing up quickly. Sometimes, these drugs can affect your body’s electrolyte balance. Your doctor will likely monitor your potassium and sodium levels with regular blood tests.
Beta-Blockers: Slowing the Heart Rate
Beta-blockers work by making your heart beat slower and with less force. They block certain natural chemicals, like adrenaline, from acting on your heart. This reduces the workload on your heart. When your heart pumps less forcefully, your blood pressure goes down.
These drugs affect “beta” receptors in your heart and blood vessels. By blocking these receptors, they stop the effects of stress hormones. This calms your cardiovascular system.
Common side effects of beta-blockers include feeling tired or fatigued. Some people notice cold hands and feet. Your heart rate will be slower, which is how the drug works. Tell your doctor if you feel unusually sluggish or notice other changes.
ACE Inhibitors: Relaxing Blood Vessels
ACE inhibitors are powerful blood pressure reducers. They target a system in your body called the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). A key player in this system is the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). This enzyme normally creates a hormone called angiotensin II, which narrows your blood vessels.
ACE inhibitors block this enzyme. They stop angiotensin II from forming. When this powerful vessel-narrowing hormone is blocked, your blood vessels relax and widen. Wider vessels mean blood flows more easily, which lowers your blood pressure.
One common side effect of ACE inhibitors is a dry, hacking cough. This cough usually does not produce mucus. It can be quite bothersome for some people. Dizziness, especially when first starting the medication, is also possible.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
ARBs work a lot like ACE inhibitors but in a slightly different way. Instead of stopping the creation of angiotensin II, ARBs block it from binding to its receptors. Think of it like a lock and key. Angiotensin II is the key, and the receptors are the lock. ARBs simply plug the lock, so the key can’t turn it. This still prevents blood vessels from narrowing.
ARBs are often prescribed if a person cannot tolerate the cough from ACE inhibitors. They are very effective at lowering blood pressure. Their side effect profile is similar to ACE inhibitors. However, the bothersome dry cough is much less common with ARBs.
Other Blood Pressure Medications
The main categories above are just part of the picture. Other medications can also help control high blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers relax blood vessels by stopping calcium from entering muscle cells in the heart and vessel walls. This makes the vessels relax and widen. Alpha-blockers relax certain muscles and small blood vessels. This allows blood to flow more freely.
Many patients need more than one type of medication. Sometimes, doctors combine different drugs to reach blood pressure goals. This is called combination therapy. Your doctor will carefully choose the right mix for you.
Managing Side Effects and Ensuring Treatment Success
Taking blood pressure medication can bring common side effects. Knowing what to expect and how to handle it helps you stick with your treatment plan.
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Many blood pressure drugs can cause some general side effects. You might feel dizzy, especially when you first stand up. Fatigue and headaches are also common. These symptoms often improve as your body adjusts to the medication. Keep a symptom diary to track how you’re feeling.
It is very important to tell your doctor about any new or bothersome side effects. They might adjust your dose or switch you to a different medication. Do not stop taking your medication on your own. Sudden stops can be dangerous, especially for high blood pressure.
Some symptoms need immediate medical help. Seek care right away if you have severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or sudden weakness. Intense dizziness or fainting also need urgent attention. Your health professional can tell you if something is serious.
Tips for Adhering to Your Medication Plan
Taking your medication consistently is key for blood pressure control. Use a pillbox to organize your daily doses. Set reminders on your phone or put a note on your fridge. Make taking your pills part of your daily routine.
Try to take your medication at the same time every day. This helps keep a steady level of the drug in your body. If you miss a dose, do not take a double dose. Just take your next dose at the regular time.
Always talk openly with your doctor or pharmacist. Ask questions about your medication. Learn about potential interactions with other drugs, vitamins, or even herbal supplements. Your healthcare team is there to support you.
Lifestyle Support for Blood Pressure Control
Medication works best when supported by a healthy lifestyle. What you eat plays a huge role. The DASH diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can significantly lower blood pressure. Cut down on sodium and eat foods high in potassium, like bananas and avocados.
Regular physical activity is also vital. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on your heart. Even small changes can make a big difference.
Don’t forget stress. Chronic stress can raise your blood pressure. Try mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Make sure you get enough sleep each night. These habits complement your medication and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding your high blood pressure medications is a powerful step. You now know about diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs. Each class works uniquely to help lower your blood pressure and protect your heart. Knowing about potential side effects helps you manage your treatment effectively.
This knowledge empowers you to take charge of your health. Your medication is a tool in your overall treatment plan. Remember, your doctor is your best resource. Talk to your healthcare provider about your specific treatment. Ask any questions you have. Together, you can successfully manage your hypertension and live a healthier life. Click here to start the journey to a lower blood pressure.